ExoplanetHub – NASA Exoplanet Archive (TAP API) Data Sync on AWS

1. Project Overview
ExoplanetHub is a modern web application for exploring confirmed exoplanets using real-time data from NASA's Exoplanet Archive.
The system combines a Next.js TypeScript frontend with a serverless AWS backend that automatically synchronizes the latest exoplanet discoveries every six hours.
This project demonstrates how scientific data can be ingested, normalized, and served dynamically without maintaining traditional servers. The result is a fully automated, cost-efficient, and highly available public dataset updated continuously through AWS EventBridge and Lambda.
Live site: https://exoplanethub.com
Source: github.com/exoplanethub/exoplanethub.com
2. Challenge / Problem
NASA's Exoplanet Archive publishes updated data on thousands of confirmed planets orbiting other stars.
The challenge was to build a self-maintaining data pipeline that could:
- Keep ExoplanetHub's dataset current within hours of NASA updates.
- Scale effortlessly without manual intervention or scheduled server maintenance.
- Provide fast, low-latency queries for thousands of objects through a public web interface.
3. Architecture Overview
Key design: EventBridge → Lambda → DynamoDB → Next.js frontend.
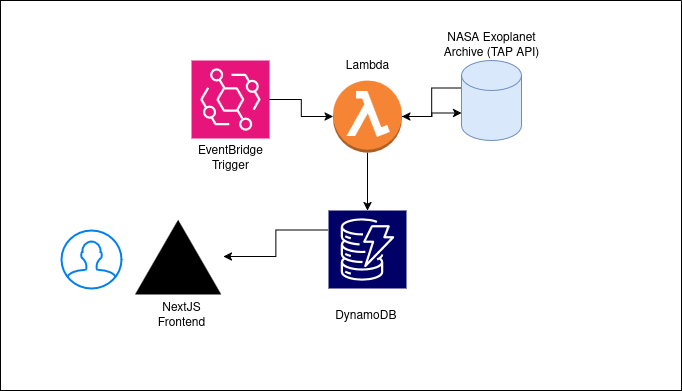
AWS Backend
- EventBridge: Runs a scheduled rule every six hours to trigger data synchronization.
- Lambda (Python 3.13): Connects to the NASA Exoplanet Archive TAP API, fetches all confirmed planet records, and performs transformation and deduplication before storing them.
- DynamoDB: Serves as the system of record with Global Secondary Indexes (GSIs) to support fast lookups and filters by host star, discovery year, or detection method.
- Cleanup Lambda: Runs nightly to archive outdated records and manage dataset size.
- SAM (Serverless Application Model): Defines all AWS resources as infrastructure-as-code for consistent deployments across dev and prod.
Frontend
- Next.js 15 (App Router) with TypeScript for type-safe rendering and data fetching.
- Direct AWS SDK access to DynamoDB for server components and API routes.
- Vercel handles frontend CI/CD, automatically deploying on pushes to
main. - GitHub Actions handle backend deployments, using tag-based workflows for dev and production.
4. Implementation Details
- Real-time ingestion: Each EventBridge rule invokes a Lambda that fetches the NASA TAP data as a CSV, parses it with Pandas, and writes normalized JSON items to DynamoDB.
- Idempotency: A hash of the
pl_name(planet name) ensures updates overwrite rather than duplicate entries. - Data structure:
{ "pk": "PLANET#Kepler-22b", "sk": "DISCOVERY#2011", "host_star": "Kepler-22", "discovery_method": "Transit", "discovery_year": 2011, "planet_radius": 2.4, "orbital_period": 289.9, "updated_at": "2025-10-08T00:00:00Z" }
5. Screenshots
 ExoplanetHub homepage
ExoplanetHub homepage
 Detailed view of an individual exoplanet with orbital and physical characteristics
Detailed view of an individual exoplanet with orbital and physical characteristics
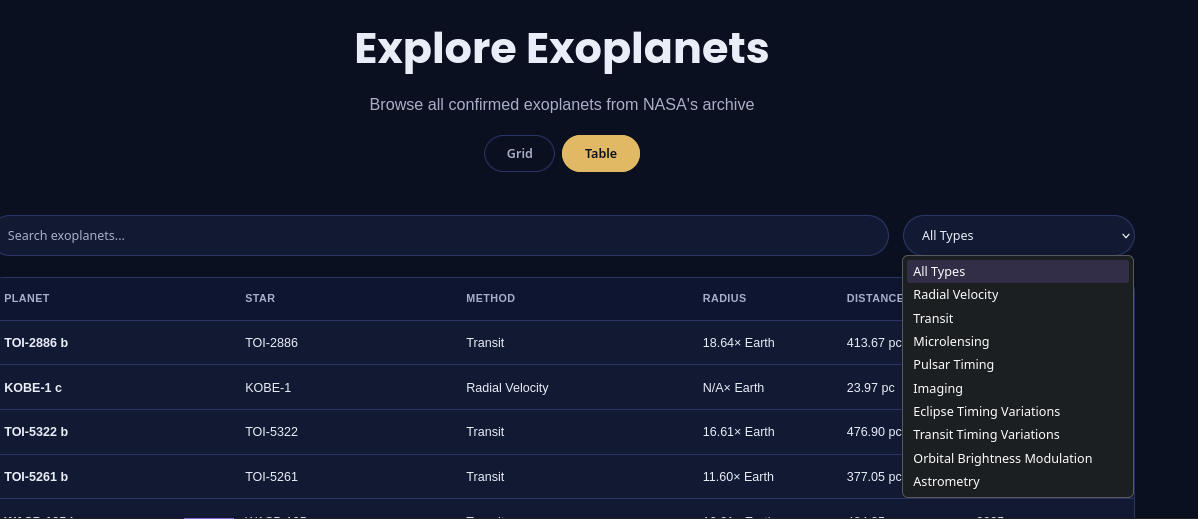 Search and filter interface for exploring the exoplanet catalog
Search and filter interface for exploring the exoplanet catalog