Building an AI-First Portfolio Site with AWS Bedrock & Agentic Tools

1. Project Overview
This portfolio site represents a fundamental shift in how personal websites can operate. Moving from static information displays to intelligent, autonomous systems that can answer questions, schedule meetings, and handle communication on behalf of their owner.
Built with Next.js 16, AWS Bedrock Knowledge Base, and Vercel AI SDK, the site features an AI assistant that serves as the primary interface for visitor interaction. Rather than forcing users to navigate through pages and forms, the assistant can retrieve contextual information, book calendar appointments, and send messages. All through natural conversation.
Live site: https://zackrylangford.com
Source: Private repository (contact for access)
2. Challenge / Problem
Traditional portfolio sites are passive. Visitors must:
- Navigate multiple pages to find information
- Fill out contact forms and wait for responses
- Manually check calendar availability for meetings
- Piece together context from scattered blog posts and project descriptions
This creates friction. It delays meaningful connection. The challenge was to build a system that could:
- Understand context from my entire body of work (blog posts, portfolio pieces, professional history)
- Take autonomous action like scheduling meetings and sending messages without manual intervention
- Maintain security while allowing AI agents to interact with backend systems
- Scale efficiently without traditional server infrastructure
3. Architecture Overview
Core pattern: RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) + Agentic Tools + Serverless Backend
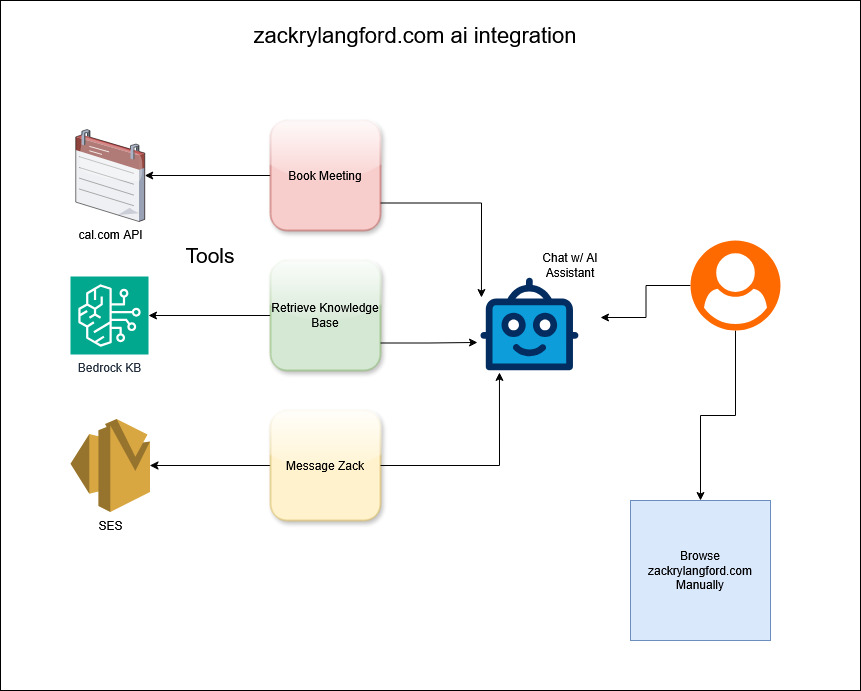
Frontend Layer
- Next.js 16 (App Router) with TypeScript for type-safe server and client components
- Vercel AI SDK for streaming chat responses and tool execution
- React hooks for chat history persistence (localStorage) and optimistic UI updates
- Markdown rendering with syntax highlighting for code examples in responses
AI Layer
- AWS Bedrock Knowledge Base: Vector search across all content (blog posts, portfolio pieces, professional history)
- OpenAI GPT4o-mini via Vercel for natural language understanding and generation
- Agentic tools for autonomous actions (booking, contact, date calculation)
- System prompt engineering with dynamic context injection and citation formatting
Integration Layer
- Cal.com API: Real-time availability checks and booking creation with Google Meet/Zoom
- AWS SES: Transactional emails for contact messages and booking confirmations
- Rate limiting: In-memory store with per-IP tracking
- RAG context retrieval: Bedrock queries based on user input to a custom knowledge base.
Data Pipeline
- TypeScript scripts to prepare and sync content to S3
- S3 bucket as knowledge base data source
- Bedrock ingestion jobs triggered automatically after content updates
- Vector embeddings generated by Bedrock for semantic search
4. Implementation Details
AWS Bedrock Knowledge Base Setup
The knowledge base is the foundation of the AI assistant's contextual awareness. I built TypeScript scripts that read markdown files from my blog and portfolio directories, enrich them with metadata (URLs, categories, slugs), and sync them to S3. When content updates, a Bedrock ingestion job automatically triggers to re-index everything with vector embeddings.
The retrieval system queries Bedrock with the user's message and returns the top 10 most relevant chunks of content. These get injected into the system prompt so the AI can cite specific blog posts and projects when answering questions.
Agentic Tool System
The AI assistant has three core capabilities implemented as tools.
Contact Message Tool:
- Collects sender name, email, and message through conversational flow
- Validates input (email format, message length under max chars)
- Sends via AWS SES with confirmation email to sender
- Requires user confirmation before sending
Booking Tools (four-tool workflow):
- calculateDateRange - Converts natural language ("tomorrow", "next week") into ISO date ranges
- checkAvailability - Queries Cal.com API for available time slots in the date range
- showBookingConfirmation - Displays booking details and waits for user confirmation
- scheduleBooking - Creates the actual calendar event via Cal.com with Google Meet or Zoom link
The booking flow asks one question at a time (name, then email, then platform preference, then optional notes) to keep the conversation natural. Cal.com handles all the heavy lifting for timezone conversion, conflict detection, and sending calendar invites.
System Prompt Engineering
The system prompt is dynamically constructed for each request with:
- Current date context for EST timezone calculations
- Agent context (latest blog post, latest project, total counts)
- Retrieved knowledge base context based on the user's query
- Step-by-step tool usage instructions
- Citation formatting rules for inline references
This ensures the AI always has fresh context and knows exactly how to use each tool.
Chat Interface
The frontend uses Vercel AI SDK's useChat hook for streaming responses. Messages are optimistically added to the UI before the API responds, then deduplicated using useMemo to prevent glitches. Chat history persists to localStorage so conversations survive page refreshes.
Rate limiting tracks requests per IP address using an in-memory Map. Simple but effective for a personal site.
5. Design Decisions & Trade-offs
Why AWS Bedrock Knowledge Base?
Pros:
- Managed vector database (no infrastructure to maintain)
- Automatic embedding generation
- Built-in chunking and indexing
- Pay-per-query pricing (cost-efficient for low traffic)
Cons:
- Less control over embedding model
- Retrieval configuration limited compared to self-hosted solutions
- Cold start latency on first query
Alternative considered: Pinecone or self-hosted Qdrant. I chose Bedrock for operational simplicity and AWS ecosystem integration.
Why Cal.com over Custom Calendar?
Pros:
- Battle-tested scheduling logic (timezone handling, conflict detection)
- Built-in integrations (Google Meet, Zoom, Google Calendar)
- Automatic confirmation emails and reminders
- No need to manage OAuth flows
Cons:
- API rate limits (60 requests/minute)
- Less customization of booking flow
- Dependency on third-party service
Trade-off: Faster time to market and reduced maintenance burden outweighed customization needs.
Why Vercel AI SDK?
Pros:
- Streaming responses out of the box
- Tool execution framework with type safety
- React hooks for chat UI
- Multi-provider support (easy to switch from Bedrock to OpenAI)
Cons:
- Opinionated patterns (less flexibility)
- Beta features can have breaking changes
Alternative considered: LangChain. I chose Vercel AI SDK for simpler API and better TypeScript support.
Why In-Memory Rate Limiting?
Pros:
- Zero infrastructure (no Redis needed)
- Instant response (no network calls)
- Simple implementation
Cons:
- Resets on server restart
- Doesn't work across multiple instances (Vercel serverless functions)
- Can be bypassed with IP rotation
Trade-off: For a personal portfolio site with low traffic, simplicity beats robustness. I'd migrate to Redis or Upstash for production scale.
6. Security Considerations
Input Validation
- Email format validation using Zod schemas
- Message length limits (2000 chars) to prevent abuse
- HMAC signature verification for webhooks (if implemented)
Rate Limiting
- Per-IP tracking
- Graceful error messages without exposing system details
API Key Management
- All credentials stored in environment variables
- No API keys exposed to client-side code
- Separate keys for dev/prod environments
Tool Guardrails
- Confirmation step before booking or sending messages
- No ability to delete or modify existing data
- Read-only access to knowledge base content
Future Enhancements
- Agent to agent authentication using API keys or OAuth for other AI agents to interact with the site
- Audit logging to track all tool executions for security monitoring
- Content filtering to prevent prompt injection attacks on knowledge base queries
7. Lessons Learned
What Worked Well
- RAG pattern is powerful. Combining retrieval with generation gives accurate, cited responses.
- Tool confirmation steps. Asking users to confirm before taking action prevents mistakes.
- One question at a time. Conversational flow feels more natural than form style data collection.
- Streaming responses. Users see progress immediately which reduces perceived latency.
What Was Challenging
- Date and timezone handling. "Tomorrow" means different things in different timezones. I solved this with explicit EST calculations in the system prompt.
- Tool execution order. Ensuring tools are called in correct sequence (like calculateDateRange before checkAvailability) required careful prompt engineering.
- Message deduplication. Optimistic UI updates caused duplicate messages. Fixed with useMemo filtering.
- Citation formatting. Getting the AI to consistently format references required multiple prompt iterations.
What I'd Do Differently
- Add observability earlier. I'd implement structured logging and metrics from day one.
- Add unit tests for tools. Tool logic is complex enough to warrant test coverage.
9. Future Roadmap
Phase 1: Enhanced Agent Capabilities
- Multi-turn booking to handle complex scheduling like "Find a time next week when both John and I are free"
- Follow-up reminders that proactively reach out to users who started but didn't complete booking
Phase 2: Agent to Agent Communication
- API endpoint for other agents to allow external AI assistants to query my availability and book meetings
- Authentication layer using API keys or OAuth for agent access
- Rate limiting per agent with separate quotas for human users versus AI agents
Phase 3: Advanced RAG
- Hybrid search that combines vector search with keyword search for better retrieval
- Re-ranking using a separate model to re-rank retrieved chunks
- Query expansion to generate multiple search queries for better coverage
Phase 4: Analytics and Insights
- Conversation analytics to track common questions, booking patterns, and drop-off points
- A/B testing to experiment with different system prompts and tool workflows
- User feedback loop that collects thumbs up or down on responses to improve over time
10. Technical Stack Summary
Frontend:
- Next.js 16 (App Router)
- TypeScript
- Vercel AI SDK
AI/ML:
- AWS Bedrock
- AWS Bedrock Knowledge Base
- Vector embeddings (Titan Embeddings)
Backend/APIs:
- Next.js API Routes
- Cal.com API
- AWS SES (email)
- AWS S3 (knowledge base storage)
Infrastructure:
- Vercel (hosting, edge functions)
- AWS (Bedrock, S3, SES)
- GitHub Actions (CI/CD for knowledge base sync)
Developer Tools:
- TypeScript
- ESLint
- pnpm (package management)
Conclusion
This project demonstrates how AI can transform a static portfolio site into an intelligent, autonomous system that provides real value to visitors. By combining RAG with agentic tools, the site can answer questions, schedule meetings, and handle communication. All through natural conversation.
The architecture is designed for scalability (serverless), maintainability (TypeScript, infrastructure as code), and extensibility (modular tool system). Most importantly, it's built with security and user experience as first class concerns.
This is just the beginning. As AI agents become more prevalent, sites like this will be the norm rather than the exception. I'm excited to continue pushing the boundaries of what's possible with agent first web design.
Want to Build Something Similar?
If you're interested in adding AI capabilities to your site or building an agent-ready system for your business, I'd love to help. Whether you need:
- Custom AI assistants with RAG
- Agentic tool systems for autonomous actions
- AWS Bedrock Knowledge Base setup
- Agent-to-agent communication protocols
Let's connect:
- Talk to my AI assistant and book a meeting
- Send me a message with your project details
- View my other projects to see more of my work
💬 Want to see the AI assistant in action?
Return here and try it out yourself,
or connect with me on 💼 LinkedIn and 🐙 GitHub.